The Ultimate Guide to Business Process Automation
Business process automation (BPA) is the use of technology to automate repeatable, multi-step business processes with minimal human intervention. Instead of employees manually handling routine tasks like data entry, approvals, or document routing, software systems execute these workflows automatically based on predefined rules and triggers.
What business process automation includes:
- Workflow automation – Routing tasks, documents, and approvals through predefined steps
- Data integration – Connecting systems to share information automatically
- Rule-based decisions – Making routine choices based on business logic
- End-to-end processes – Handling complete workflows from start to finish
- Real-time monitoring – Tracking progress and identifying bottlenecks
As Bill Gates once said, “Automation applied to an efficient operation will magnify the efficiency.” But here’s the reality: 80% of business leaders now cite automation as a core priority, according to Gartner research. The reason is simple – companies using automation achieve 2.3x higher ROI and 3.7x more cost savings than those that don’t.
For retail business owners, this isn’t just about cutting costs. It’s about empowering your team to focus on customers instead of paperwork. It’s about scaling your operations without proportionally increasing your headcount. And it’s about staying competitive in a digital-first world.
The best part? Modern automation tools use low-code platforms that don’t require technical expertise. Your team can build and manage automated workflows using simple drag-and-drop interfaces.
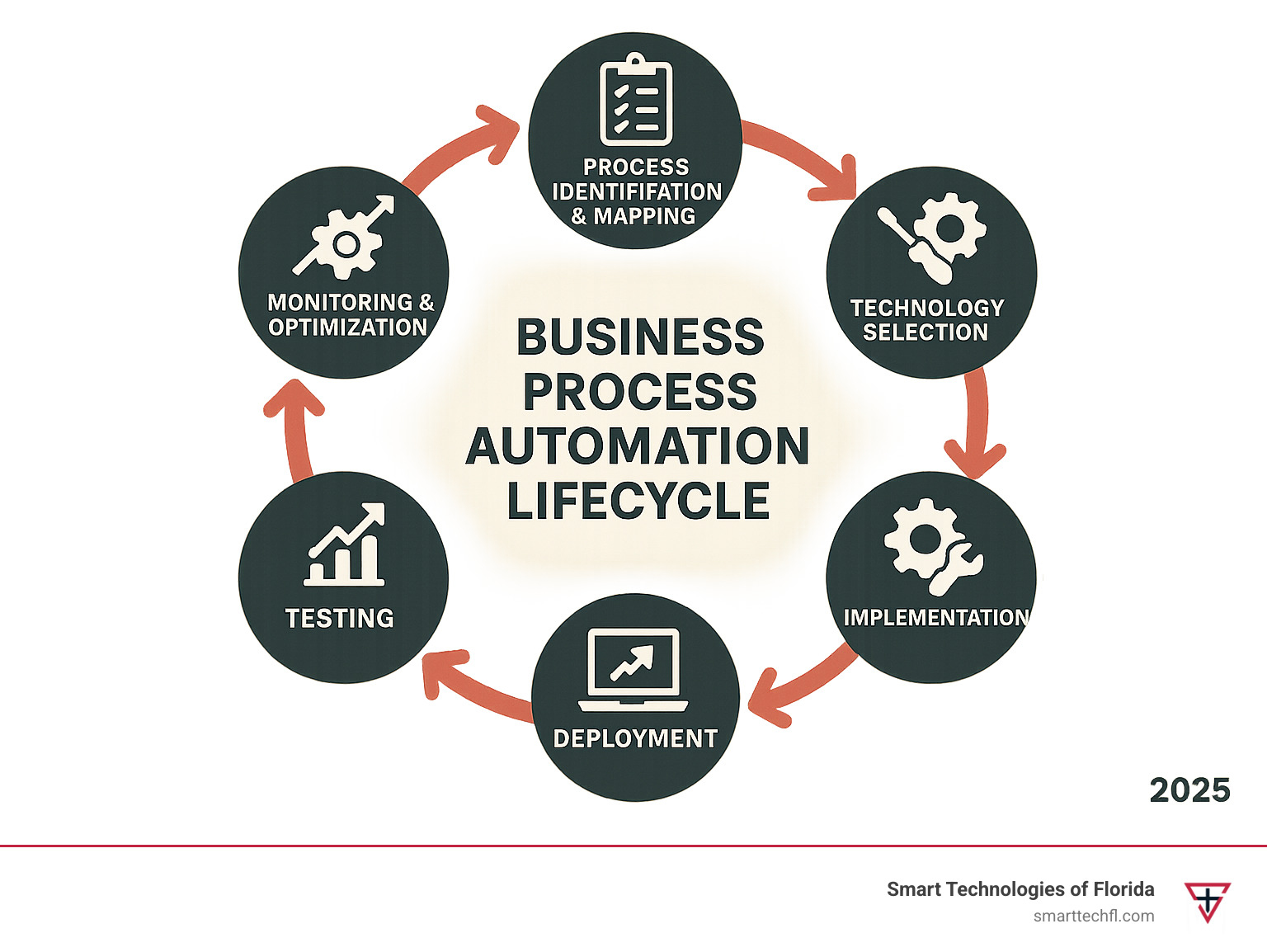
Understanding Business Process Automation
The origins of business process automation trace back to Business Process Management (BPM) practices that emerged in the 1990s. However, today’s BPA has evolved far beyond simple workflow routing. Modern automation combines artificial intelligence, machine learning, and cloud technologies to create intelligent systems that can adapt and learn.
At its core, BPA transforms how work flows through your organization. Instead of tasks sitting in email inboxes or paper forms getting lost on desks, automated processes ensure consistent execution every time. This change requires understanding three fundamental concepts:
Process mapping forms the foundation of any automation initiative. We need to document every step, decision point, and handoff in your current workflows. This isn’t just about drawing flowcharts – it’s about understanding the “why” behind each action and identifying opportunities for improvement.
The technology stack for modern BPA includes workflow engines, data integration platforms, AI-powered decision tools, and user-friendly interfaces. These components work together to create seamless automation experiences that feel natural to your team.
Scalability ensures your automation grows with your business. Well-designed automated processes can handle increased volume without proportional increases in resources, making them essential for growing organizations.
What Is Business Process Automation?
Business process automation encompasses the strategic use of technology to execute complex, multi-step workflows with minimal human intervention. Unlike simple task automation, BPA orchestrates entire business processes from initiation to completion.
Think of it this way: if a customer places an order on your website, traditional manual processes might involve five different people checking inventory, processing payment, updating records, scheduling shipping, and sending confirmation emails. With BPA, this entire sequence happens automatically within minutes of the order being placed.
Rule-based workflows form the backbone of BPA systems. These are the “if-then” statements that guide automated decisions. For example: “If order value exceeds $500, then route to manager for approval.” These rules capture your business logic and ensure consistent application across all transactions.
End-to-end automation means handling complete business processes, not just individual tasks. This might involve integrating your e-commerce platform with inventory management, payment processing, shipping systems, and customer communication tools to create a seamless order fulfillment process.
Data integration ensures information flows smoothly between different systems without manual data entry. When your CRM automatically updates with shipping information from your logistics provider, that’s data integration in action.
How Business Process Automation Powers Digital Change
Business process automation serves as the engine of digital change, enabling organizations to respond quickly to market changes and customer demands. Research shows that companies with mature automation strategies demonstrate significantly higher agility in adapting to business disruptions.
Agility comes from having processes that can scale up or down based on demand. During peak seasons, automated systems handle increased volume without the delays associated with hiring and training additional staff. When demand decreases, you’re not stuck with excess capacity.
Customer experience improves dramatically when automation eliminates delays and errors. Customers receive instant confirmations, accurate order tracking, and timely updates without human intervention. This consistency builds trust and loyalty.
Productivity gains emerge as employees shift from routine tasks to value-adding activities. Instead of spending hours on data entry, your team can focus on customer service, strategic planning, and business development.
Compliance becomes more manageable with automated audit trails and standardized processes. Every action is logged, every decision is documented, and regulatory requirements are consistently met without relying on human memory or diligence.
Scientific research on automation ROI demonstrates that organizations achieving the highest returns from automation share three characteristics: organization-wide adoption, people-centric technology implementation, and focus on scalability.
BPA vs. RPA vs. BPM: Key Differences & Synergies
Understanding the taxonomy of automation technologies helps you make informed decisions about which approach best serves your needs. While these terms are often used interchangeably, they represent different levels and types of automation.
Task automation focuses on individual, repetitive activities like data entry or file transfers. Workflow orchestration coordinates multiple tasks and systems to complete entire business processes. Strategic governance provides the framework for managing and optimizing processes organization-wide.
Hyperautomation represents the convergence of these approaches, combining multiple technologies to create intelligent, adaptive systems that can handle complex scenarios with minimal human oversight.
| Aspect | BPA | RPA | BPM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scope | End-to-end processes | Individual tasks | Organization-wide process management |
| Complexity | High – integrates multiple systems | Medium – mimics human actions | High – strategic framework |
| Implementation | Requires process redesign | Quick deployment | Long-term initiative |
| Technology | APIs, workflows, AI | Software robots, UI interaction | Modeling, analysis, optimization |
| Best For | Complex multi-step processes | Repetitive, rule-based tasks | Process governance and improvement |
Business Process Automation vs. Robotic Process Automation
Business process automation and Robotic Process Automation (RPA) serve different purposes in the automation landscape. While both reduce manual work, they operate at different levels of complexity and integration.
RPA deploys software robots that mimic human interactions with computer systems. These bots can log into applications, copy and paste data, click buttons, and perform other routine tasks exactly as a human would. RPA excels at automating repetitive, rule-based activities that don’t require significant changes to existing systems.
UI integration is RPA’s primary strength. Bots interact with applications through their user interfaces, making RPA ideal for situations where you can’t modify underlying systems or access APIs. This approach enables rapid deployment but can be fragile when user interfaces change.
API integration represents BPA’s advantage over RPA. Instead of mimicking human actions, BPA connects systems directly through their application programming interfaces. This creates more robust, scalable automation that’s less likely to break when software updates occur.
Unattended bots can run 24/7 without human supervision, handling high-volume, predictable tasks. However, they require well-defined processes and clear exception handling procedures to operate effectively.
The key difference lies in scope and sophistication. RPA automates tasks; business process automation orchestrates entire workflows that may include RPA components alongside other technologies.
Business Process Automation within Business Process Management
Business process automation operates most effectively within a broader Business Process Management (BPM) framework. BPM provides the strategic context and governance structure that ensures automation initiatives align with organizational goals.
Process modeling in BPM creates the blueprints that guide automation implementation. These models document current state processes, identify improvement opportunities, and design future state workflows that incorporate automation.
Continuous improvement cycles ensure automated processes remain optimized over time. Regular reviews identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and opportunities for improvement. This iterative approach prevents automation from becoming rigid or outdated.
KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) provide the metrics needed to measure automation success. These might include cycle time reduction, error rates, cost savings, and customer satisfaction scores. Without proper measurement, it’s impossible to demonstrate automation value or identify areas for improvement.
Governance frameworks establish standards for automation development, deployment, and maintenance. This includes security protocols, compliance requirements, change management procedures, and performance monitoring standards.
The synergy between BPA and BPM creates a powerful combination where strategic process management guides tactical automation implementation, resulting in sustainable, scalable improvements.
Benefits & Proven ROI of Business Process Automation
The financial and operational benefits of business process automation extend far beyond simple cost reduction. Organizations implementing comprehensive automation strategies report transformative impacts across multiple dimensions of their business.
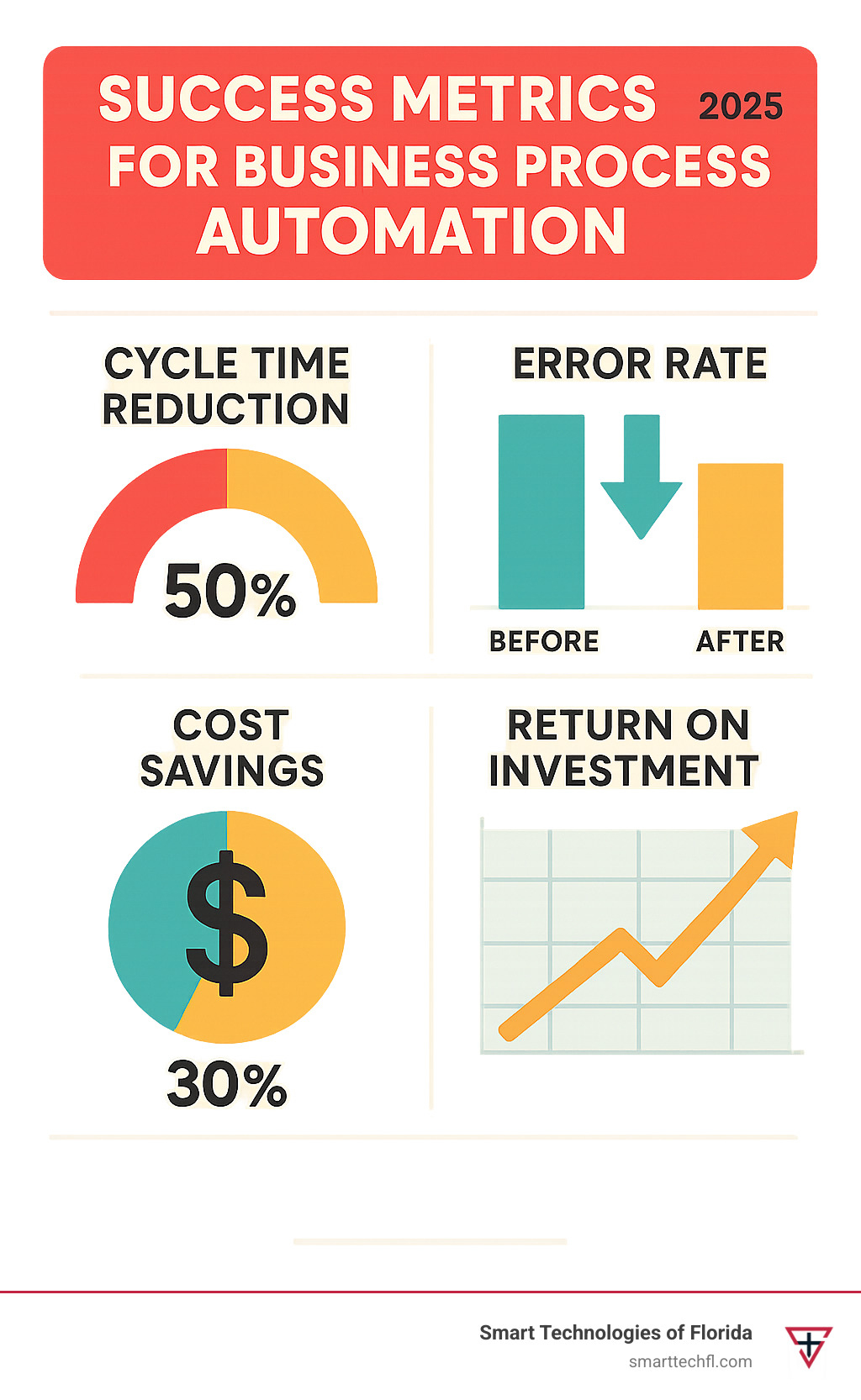
Efficiency gains typically range from 20-50% reduction in process cycle times. Tasks that previously took hours or days can often be completed in minutes through automation. This acceleration enables faster customer service, quicker decision-making, and more responsive operations.
Cost savings emerge from reduced labor requirements, fewer errors, and improved resource utilization. However, the most significant savings often come from enabling growth without proportional increases in administrative overhead.
Error reduction dramatically improves quality and compliance. Automated processes follow predefined rules consistently, eliminating the human errors that plague manual workflows. This reliability is particularly valuable in regulated industries where mistakes can result in significant penalties.
Employee engagement often improves when automation eliminates tedious, repetitive tasks. Staff can focus on more meaningful work that uses their skills and creativity. This shift typically leads to higher job satisfaction and reduced turnover.
Revenue growth becomes possible when automation frees up resources for customer-facing activities and strategic initiatives. Companies can pursue new opportunities without being constrained by administrative bottlenecks.
Audit trails provide complete visibility into process execution, supporting compliance requirements and enabling data-driven process improvements.
Business process automation research indicates that successful implementations share common characteristics: clear objectives, stakeholder buy-in, and phased rollout strategies.
Quantifying the Impact of Business Process Automation
Measuring the impact of business process automation requires both quantitative metrics and qualitative assessments. The most successful organizations establish baseline measurements before implementation and track improvements over time.
Metrics should cover efficiency, quality, cost, and customer satisfaction dimensions. Common measurements include:
- Cycle time – How long processes take from start to finish
- Throughput – How many transactions are processed per unit of time
- Error rates – Frequency of mistakes or rework requirements
- Cost per transaction – Total cost divided by number of processes completed
- Customer satisfaction – Feedback scores and complaint rates
Net present value (NPV) calculations help justify automation investments by comparing costs and benefits over time. Most automation projects show positive NPV within 6-18 months, with returns accelerating as processes scale.
The key is establishing a measurement framework before implementation begins. This enables accurate before-and-after comparisons and provides data to guide optimization efforts.
Cultural & Workforce Gains from Business Process Automation
Business process automation creates significant cultural and workforce benefits that often exceed the direct operational improvements. These human-centered gains contribute to long-term organizational success and sustainability.
Job satisfaction typically increases when employees are freed from repetitive, mind-numbing tasks. Staff can focus on problem-solving, customer interaction, and creative work that provides greater fulfillment and professional development opportunities.
Upskilling becomes possible when automation handles routine work. Employees can develop new capabilities in areas like data analysis, process improvement, and technology management. This professional growth benefits both individuals and organizations.
Change management is crucial for realizing these benefits. Successful automation implementations involve employees in the design process, provide comprehensive training, and clearly communicate how automation will improve rather than replace human contributions.
At Smart Technologies of Florida, we’ve observed that organizations with people-centric automation approaches achieve higher adoption rates and better long-term results. Our 23 years of experience has shown that technology succeeds when it empowers people rather than replacing them.
Selecting Processes & Technologies to Automate
Choosing the right processes and technologies for automation determines the success of your business process automation initiative. Not all processes are suitable for automation, and not all technologies are appropriate for every situation.
Process mining tools help identify automation opportunities by analyzing how work actually flows through your organization. These tools reveal bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and variations that may not be apparent through traditional process documentation.
Suitability criteria for automation include:
- High volume and frequency
- Well-defined rules and procedures
- Minimal exceptions or variations
- Clear inputs and outputs
- Significant time investment
- Error-prone manual steps
Low-code platforms enable business users to build and modify automated workflows without extensive programming knowledge. These tools democratize automation by putting process improvement capabilities directly in the hands of process owners.
AI/ML capabilities improve automation by enabling systems to handle unstructured data, make intelligent decisions, and continuously improve performance. However, these advanced features require careful consideration of data quality and governance requirements.
Cloud platforms provide the scalability and flexibility needed for modern automation. Cloud-based solutions offer faster deployment, automatic updates, and the ability to scale resources based on demand.
More info about Streamlining Business Processes provides additional guidance on identifying and prioritizing automation opportunities.
High-Value Use Cases for Business Process Automation
Certain types of processes consistently deliver high returns when automated. These business process automation use cases have proven successful across multiple industries and organization sizes.
HR onboarding automation can reduce new employee processing time from weeks to days while ensuring consistent completion of all required steps. Automated workflows handle document collection, system access provisioning, training scheduling, and compliance verification.
Accounts payable processes benefit significantly from automation. Invoice processing, approval routing, payment scheduling, and vendor communications can be streamlined to reduce processing time by 50-70% while improving accuracy and compliance.
Customer onboarding automation ensures consistent, professional experiences for new clients. Automated workflows can handle account setup, document collection, compliance verification, and initial service delivery coordination.
Compliance processes often involve repetitive checking, reporting, and documentation activities that are ideal for automation. Automated compliance monitoring can identify issues proactively and ensure consistent adherence to regulatory requirements.
The key to success with these use cases is starting with well-documented, stable processes and gradually expanding automation scope as confidence and capabilities grow.
Toolbox: From Low-Code Platforms to Intelligent Automation
Modern business process automation relies on a diverse toolkit of technologies that can be combined to create comprehensive solutions. Understanding these tools helps you make informed decisions about your automation strategy.
RPA suites provide the software robots and management capabilities needed for task-level automation. These platforms typically include bot development tools, scheduling capabilities, and monitoring dashboards.
Workflow engines orchestrate complex processes that span multiple systems and involve human decision points. These tools provide the visual design capabilities and execution infrastructure needed for end-to-end process automation.
Analytics platforms provide the insights needed to optimize automated processes. These tools track performance metrics, identify bottlenecks, and suggest improvements based on actual process execution data.
Connectors enable integration between different systems and applications. Pre-built connectors for popular business applications can significantly reduce implementation time and complexity.
More info about Automation Tools offers detailed guidance on selecting and implementing automation technologies.
Implementation Roadmap & Best Practices
Successful business process automation implementation requires careful planning, stakeholder engagement, and systematic execution. Organizations that follow structured approaches achieve better results with fewer disruptions.
Stakeholder buy-in is essential for automation success. This includes executive sponsorship, process owner participation, and end-user support. Clear communication about automation benefits and impacts helps build the coalition needed for successful implementation.
Pilot projects provide opportunities to test automation approaches, refine processes, and demonstrate value before full-scale deployment. Successful pilots build confidence and provide lessons learned that improve subsequent implementations.
Iterative scaling allows organizations to expand automation gradually, incorporating lessons learned and building capabilities over time. This approach reduces risk and enables continuous improvement.
Security considerations must be addressed throughout the automation lifecycle. This includes data protection, access controls, audit trails, and compliance with relevant regulations.
Governance frameworks ensure automation initiatives align with organizational standards and objectives. This includes change management procedures, performance monitoring, and continuous improvement processes.
7-Step Framework to Deploy Business Process Automation
This proven framework provides a systematic approach to business process automation implementation that minimizes risk while maximizing value.
Step 1: Assess your current processes to identify automation opportunities. Document existing workflows, measure current performance, and prioritize processes based on potential impact and implementation complexity.
Step 2: Optimize processes before automating them. Remove unnecessary steps, clarify decision points, and standardize procedures. As Bill Gates noted, automating inefficient processes simply makes them inefficiently automated.
Step 3: Automate selected processes using appropriate technologies. Start with simple, high-impact processes and gradually expand to more complex scenarios as capabilities mature.
Step 4: Measure performance against established baselines. Track key metrics like cycle time, error rates, cost per transaction, and user satisfaction to quantify automation benefits.
Step 5: Refine processes based on performance data and user feedback. Automation is not a “set it and forget it” solution – continuous improvement is essential for long-term success.
Step 6: Sustain automation benefits through ongoing governance and support. This includes regular reviews, updates for changing business requirements, and expansion to new opportunities.
Step 7: Scale successful automation approaches across the organization. Use lessons learned from initial implementations to accelerate deployment in other areas.
Measuring Success & Avoiding Common Pitfalls
Effective measurement is crucial for demonstrating business process automation value and identifying improvement opportunities. However, many organizations make common mistakes that undermine their automation initiatives.
KPI dashboards should provide real-time visibility into automation performance. Key metrics include process cycle time, throughput, error rates, cost savings, and user satisfaction scores.
ROI tracking requires careful attention to both costs and benefits. Implementation costs include software licenses, development time, training, and ongoing maintenance. Benefits include labor savings, error reduction, faster cycle times, and improved customer satisfaction.
Risk mitigation involves identifying potential failure points and developing contingency plans. Common risks include system integration challenges, process exceptions, and user adoption issues.
Continuous improvement processes ensure automation remains effective as business requirements evolve. Regular reviews should assess performance, identify optimization opportunities, and plan for future improvements.
Common pitfalls to avoid include:
- Automating broken processes without fixing them first
- Underestimating change management requirements
- Focusing only on cost reduction instead of value creation
- Neglecting security and compliance considerations
- Failing to involve end users in design and testing
Future Trends & Innovations in Business Process Automation
The future of business process automation is being shaped by advances in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and cloud computing. These technologies are enabling new levels of automation sophistication and intelligence.
Intelligent automation combines traditional workflow automation with AI capabilities to handle unstructured data, make complex decisions, and adapt to changing conditions. This evolution enables automation of processes that previously required human judgment.
Process mining technologies automatically find how processes actually work by analyzing system logs and user interactions. This capability accelerates automation implementation and identifies optimization opportunities that might otherwise be missed.
Generative AI is beginning to transform automation by enabling systems to create content, generate responses, and even design new processes. This technology has the potential to automate creative and analytical tasks that were previously thought to require human intelligence.
Autonomous processes represent the ultimate goal of automation – systems that can operate independently, make decisions, and adapt to new situations without human intervention. While still emerging, these capabilities are beginning to appear in specific domains.
Sustainability considerations are driving automation initiatives focused on reducing resource consumption, minimizing waste, and optimizing energy usage. Green automation is becoming an important consideration for environmentally conscious organizations.
From Business Process Automation to Hyperautomation
Hyperautomation represents the next evolution of business process automation, combining multiple technologies to create comprehensive automation ecosystems. This approach goes beyond individual process automation to orchestrate entire business functions.
Orchestration platforms coordinate multiple automation tools, systems, and processes to create seamless end-to-end experiences. These platforms provide the integration layer needed to connect different automation technologies.
Decision engines enable automated systems to make complex choices based on business rules, data analysis, and machine learning insights. These capabilities extend automation to processes that require judgment and decision-making.
Predictive analytics allow automated systems to anticipate future needs and proactively take action. This might include automatically ordering inventory based on demand forecasts or scheduling maintenance before equipment failures occur.
The transition to hyperautomation requires careful planning and gradual implementation. Organizations should build foundational automation capabilities before attempting more complex orchestration scenarios.
Emerging Standards & Governance for Business Process Automation
As business process automation becomes more prevalent, new standards and governance frameworks are emerging to ensure responsible and effective implementation.
Ethics considerations include ensuring automation decisions are fair, transparent, and aligned with organizational values. This is particularly important when automation affects customer interactions or employee opportunities.
Transparency requirements are increasing, especially in regulated industries. Organizations must be able to explain how automated decisions are made and provide audit trails for compliance purposes.
Regulatory compliance is becoming more complex as automation spans multiple jurisdictions and industries. Organizations must ensure their automation practices meet all applicable legal and regulatory requirements.
These emerging standards emphasize the importance of human oversight, explainable AI, and responsible automation practices that benefit all stakeholders.
Frequently Asked Questions about Business Process Automation
What types of processes are best suited for automation?
The best candidates for business process automation are processes that are:
- High volume – Performed frequently throughout the day or week
- Rule-based – Follow clear, consistent procedures with minimal exceptions
- Time-sensitive – Have deadlines or service level requirements
- Error-prone – Currently experience quality issues due to manual handling
- Well-documented – Have clear procedures and defined inputs/outputs
Examples include invoice processing, employee onboarding, customer service inquiries, inventory management, and compliance reporting. Avoid automating processes that are highly variable, require significant human judgment, or are poorly defined.
How do we calculate ROI for business process automation projects?
ROI calculation for business process automation should include both direct and indirect benefits:
Direct Benefits:
- Labor cost savings from reduced manual effort
- Error reduction and associated cost avoidance
- Faster cycle times enabling increased throughput
- Reduced compliance and audit costs
Indirect Benefits:
- Improved customer satisfaction and retention
- Employee productivity gains from focusing on higher-value work
- Scalability benefits from handling growth without proportional staff increases
- Better decision-making from improved data quality and availability
Implementation Costs:
- Software licenses and implementation services
- Training and change management
- Ongoing maintenance and support
- System integration and customization
Most organizations see positive ROI within 6-18 months, with returns accelerating as automation scales across the organization.
Will business process automation replace human jobs?
Business process automation typically transforms jobs rather than eliminating them entirely. While automation handles routine, repetitive tasks, it creates opportunities for employees to focus on higher-value activities that require human skills like:
- Customer relationship management
- Strategic planning and analysis
- Creative problem-solving
- Complex decision-making
- Process improvement and optimization
Organizations that implement automation successfully invest in employee training and development to help staff transition to these new roles. The goal is to augment human capabilities rather than replace them.
Research shows that companies with people-centric automation approaches achieve better results and higher employee satisfaction than those that focus solely on cost reduction.
Conclusion
Business process automation represents a transformative opportunity for organizations ready to accept digital change. The evidence is clear: companies that implement comprehensive automation strategies achieve higher ROI, better operational efficiency, and improved customer satisfaction.
The key to success lies in taking a strategic, people-centric approach that focuses on empowering your team rather than simply reducing costs. This means starting with well-defined processes, involving stakeholders throughout implementation, and maintaining a focus on continuous improvement.
At Smart Technologies of Florida, we’ve spent 23 years helping organizations steer digital change challenges. Our people-centric approach ensures that automation initiatives align with your unique goals and culture while delivering measurable business value.
The future belongs to organizations that can combine human creativity and judgment with the speed and consistency of automated processes. By implementing business process automation thoughtfully and strategically, you can position your organization for sustainable growth and competitive advantage.
Ready to explore how automation can transform your business? More info about Business Process Automation Solutions provides detailed information about our services and approach. We’re here to help you open up the full potential of automation while keeping your people at the center of your change journey.












