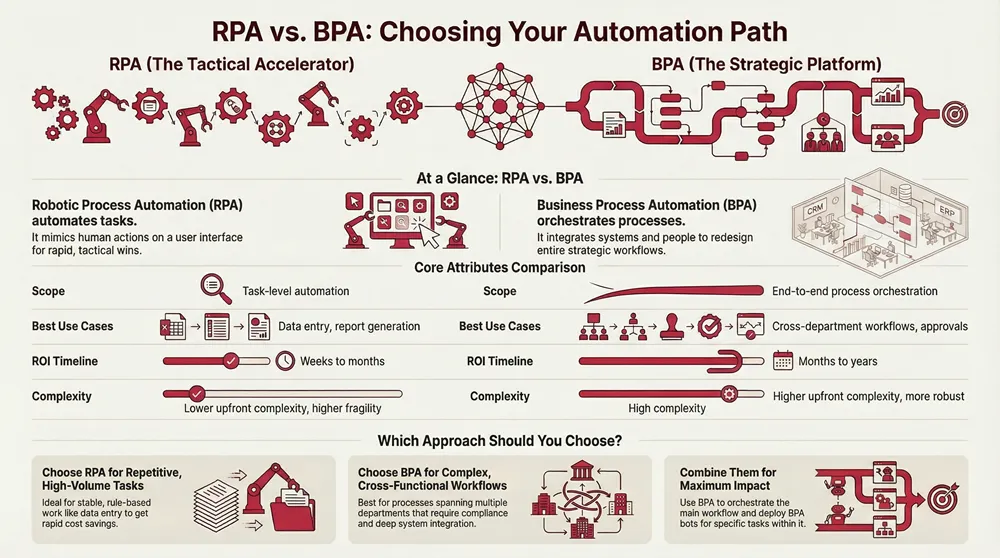
RPA vs Business Process Automation
AI Overview:
This article explains the difference between RPA, which automates single repetitive tasks, and BPA, which automates entire end-to-end workflows. RPA delivers quick, tactical wins for rule-based work, while BPA provides deeper, long-term process improvement through orchestration, integration, and analytics. The guide compares both approaches, shows how they complement each other, and offers a simple decision framework to choose RPA, BPA, or a hybrid strategy based on process complexity, volume, and integration needs. It also highlights real-world use cases and how Smart Technologies supports businesses with custom automation solutions.
RPA vs Business Process Automation: Key differences and how to choose the right automation solution
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Business Process Automation (BPA) both speed digital transformation, but they operate at different layers of an organization. This article breaks down RPA vs. BPA in clear, practical terms so you can see where task-level bots and end-to-end workflow platforms each add value. You’ll get concise definitions, how each technology works, typical benefits, and industry use cases — plus a decision framework to help you pick RPA, BPA, or a hybrid path. We also cover governance, integration patterns, and measurable outcomes (cycle time, error rates, etc.) so non-technical leaders can prioritize the highest-impact initiatives.
What is Business Process Automation and How Does It Optimize Workflows?
Business Process Automation (BPA) is a strategic approach that automates entire workflows end-to-end by combining orchestration, document management, and system integration. BPA starts with mapping processes, applies routing and decision rules, and connects systems via APIs or connectors to eliminate manual handoffs and reduce delays between departments. The payoff is faster cycle times, fewer errors, and clearer audit trails — all of which improve customer experience and compliance. With process mining and analytics, BPA becomes a continuous improvement program rather than a one-off fix: it identifies bottlenecks, measures impact, and lets teams evolve workflows based on data.
What Are the Core Principles and Components of BPA?
BPA is built on four core components: process mapping, document management, workflow orchestration, and analytics-driven process mining. Process mapping captures tasks, decision points, and handoffs so you redesign before you automate — preventing inefficient processes from being automated as-is. Document management secures and indexes content to support approvals and records retention. Orchestration engines coordinate interactions between systems using APIs and connectors. And process mining provides data-driven insight to prioritize automation where it delivers the best operational ROI.
Below are the primary BPA components and the operational benefits they deliver.
- Process mapping — documents steps, decisions, and owners to enable redesign and reliable automation.
- Document management — secures, indexes, and automates content-driven work like approvals and recordkeeping.
- Workflow orchestration — ties systems and people together for seamless end-to-end flows.
- Process mining — analyzes event logs to expose bottlenecks and variation, guiding improvement work.
This component view shows why BPA focuses on holistic outcomes and continuous improvement instead of replacing isolated tasks.
BPA components mapped to typical operational benefits:
How Does BPA Drive Efficiency and Cost Reduction in Businesses?
BPA cuts manual processing by automating multi-step workflows that span people and systems, directly lowering labor hours and operational costs. Eliminating repetitive handoffs reduces error rates and rework, which lowers cost per transaction and increases throughput. Faster, more predictable processes also shorten customer wait times and improve SLA performance, boosting retention and revenue resilience. Measurement matters: teams track KPIs such as cycle time, first-pass yield, and cost per process to quantify BPA impact and to prioritize follow-on automations for the best return.
Key measurable benefits delivered by BPA include:
- Shorter cycle times and higher throughput.
- Fewer errors and lower rework costs.
- Improved compliance and auditability through structured data capture.
These benefits create the environment where tactical RPA can plug into orchestrated workflows and deliver immediate, targeted value. The next section explains how RPA handles task-level automation and how bots are designed to run rule-based work efficiently.
What is Robotic Process Automation and How Does It Automate Repetitive Tasks?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) automates repetitive, rule-based tasks by mimicking how a person interacts with software — either at the user interface or via APIs when available. RPA bots follow defined steps like reading data, entering values, and copying records. They can run unattended on servers or work alongside employees in attended mode. RPA’s main strengths are speed of deployment and fast ROI for stable, well-defined tasks. Its dependence on interfaces can make bots fragile when UIs change, so governance and monitoring are essential for sustainable automation.
How Do RPA Bots Work to Automate Rule-Based Tasks?
RPA bots execute a programmed sequence of actions triggered by a schedule, an event, or a user. Common tasks include data extraction, form filling, and report generation. Attended bots assist staff at the desktop during busy periods, while unattended bots process batch work overnight or at scale. Typical deployment steps are process selection, bot design, testing on sample data, and production monitoring to ensure reliability. Example: a bot pulls invoice data from emails, validates fields against business rules, posts entries to the ERP, and flags exceptions for human review.
RPA deployment patterns include:
- Attended bots — speed up front-line desktop work during peaks.
- Unattended bots — run autonomously for high-volume batch processing.
- Hybrid patterns — bots handle routine steps and hand off exceptions to people.
These patterns help you decide when RPA is the practical, fast option versus when a broader BPA approach is needed.
What Are the Benefits and Limitations of RPA?
RPA delivers fast time-to-value by automating repetitive tasks with minimal disruption to existing systems. Typical gains include faster processing, improved accuracy, and quick configuration compared with deep system integrations. Limitations include sensitivity to UI changes, limited visibility across end-to-end processes, and ongoing maintenance when underlying applications change. Strong governance, version control, and integrating bots with orchestration platforms reduce these risks and prevent brittle, hard-to-maintain automation sprawl.
Pros and cons of RPA summarized:
- Pros: rapid deployment, immediate cost savings, consistent execution.
- Cons: fragile to UI changes, limited process-wide visibility, maintenance overhead.
- Mitigations: governance, version control, and pairing RPA with APIs or BPA platforms.
With both approaches defined, the next section compares them side-by-side so leaders can weigh scope, complexity, and fit.
What Are the Key Differences Between RPA and BPA?
The primary difference is scope: RPA targets task-level automation, while BPA focuses on end-to-end process orchestration that includes people, systems, and analytics. RPA shortcuts manual tasks by simulating human actions — a fast solution for high-volume, stable tasks that don’t need redesign. BPA rethinks and connects cross-functional workflows via APIs or connectors, delivering deeper transformation but requiring upfront analysis. That also affects ROI timing: RPA often yields quicker, narrower wins; BPA delivers broader, longer-term efficiency gains.
How Do RPA and BPA Differ in Scope, Complexity, and Integration?
Scope, integration depth, and governance requirements differ significantly. RPA’s scope is narrow — bots act on specific screens or APIs — so integration complexity is lower but the solution can be brittle when UIs change. BPA requires enterprise-level integration, API work, data mapping, and governance to manage cross-department processes. Governance under BPA typically means defined process owners, SLAs, and analytics; RPA governance focuses on bot lifecycle management and monitoring to prevent drift and control maintenance costs.
Key attribute differences include:
- Scope: task-level (RPA) vs. process-level (BPA).
- Integration: UI-focused and connectors (RPA) vs. API-driven system integration (BPA).
- Governance: bot lifecycle management vs. process ownership and analytics.
Can You See a Side-by-Side Comparison of RPA vs BPA?
Use the table below to quickly compare attributes and decide which approach fits your goals and constraints.
This comparison shows RPA as a tactical accelerator and BPA as a strategic platform; most organizations get the best results from a governed mix that balances speed and sustainability.
How Do RPA and BPA Complement Each Other for Enhanced Business Efficiency?
RPA and BPA work best when combined: BPA provides orchestration, visibility, and integration, while RPA fills task-level gaps where APIs aren’t available or where a quick tactical win is needed. BPA defines the process flow and data model; RPA executes repetitive steps inside that flow to remove manual effort fast. Together they deliver immediate productivity gains and longer-term resilience, because orchestration reduces the fragility of UI-based automations and centralizes monitoring and exception handling. A governed hybrid approach turns tactical wins into repeatable, scalable digital transformation.
When Should Businesses Use RPA, BPA, or Both Together?
Decide based on process scope and goals: choose RPA when tasks are repetitive, rule-based, and well-bounded; choose BPA when workflows span systems or departments and need redesign for efficiency or compliance. Use a hybrid approach when some processes need quick task automation while the broader workflow is modernized over time. Example: start with RPA for high-volume invoice entry to capture immediate savings, then migrate to an end-to-end procure-to-pay BPA to realize systemic improvement. The key is a phased rollout with governance and measurable KPIs.
A short decision checklist for choosing an automation approach:
- Assess process complexity and cross-system dependencies.
- Measure transaction volume and variability to estimate ROI timing.
- Evaluate integration options (APIs vs legacy UIs) and maintenance capacity.
- Prioritize governance and monitoring before scaling automation.
How Does Integrating RPA with BPA Workflows Improve Digital Transformation?
From a technical view, integration embeds RPA bots as activities inside an orchestrated BPA workflow so the orchestration engine can trigger bots, manage exceptions, and surface analytics across the process. Organizationally, integration aligns process owners and IT around shared KPIs and continuous improvement. Combined deployments reduce handoffs, centralize monitoring, and accelerate measurable outcomes like shorter cycle times and fewer errors. A well-governed hybrid solution turns tactical automation gains into sustainable digital transformation that can scale across the enterprise.
The next section outlines industry-specific examples and measurable use cases where RPA and BPA deliver concrete results.
What Are Real-World Use Cases and Benefits of RPA and BPA?
RPA and BPA both deliver measurable benefits, especially where processes are document-heavy, compliance-sensitive, or high-volume. In automotive and dealership operations, BPA streamlines finance and service workflows while RPA moves data between legacy systems and CRM platforms. In finance, automated reconciliations and exception handling speed close cycles and reduce audit effort. Healthcare sees faster claims processing and better accuracy when document management is combined with bots that extract and validate data. These examples follow the pattern: process mining → identifies bottlenecks → increases throughput and reduces cost.
Which Industries Benefit Most from BPA Solutions?
Industries with large document volumes, strict regulation, and frequent handoffs gain the most from BPA. Automotive dealerships, healthcare providers, financial services, manufacturing, and legal firms benefit because BPA reduces manual reconciliation, strengthens compliance, and speeds customer response. For instance, automotive operations often need enterprise integration across inventory, sales, and service — a natural fit for BPA to coordinate cross-system processes and reduce admin overhead.
Industries and why BPA fits them:
- Automotive / dealerships: integrates sales, service, and finance workflows.
- Healthcare: automates patient intake, claims processing, and records management.
- Finance: improves reconciliation, reporting, and audit readiness.
- Manufacturing: streamlines order-to-cash and supply-chain coordination.
- Legal: automates document routing and compliance tracking.
These industry patterns point to specific, high-value automation targets.
How Does RPA Automate Repetitive Tasks Across Business Functions?
RPA excels at function-level tasks like accounts payable data entry, HR onboarding form completion, IT ticket triage, and routine customer service updates. Bots can extract invoice data, populate HR systems, route tickets, and generate standard reports — delivering predictable time savings and higher accuracy. Typical ROI traits include quick payback for high-volume tasks, measurable drops in processing time per item, and fewer costly exceptions and rework.
Common functional RPA applications include:
- Accounts payable automation to shorten invoice processing.
- HR onboarding to speed employee setup and benefits enrollment.
- IT ticket triage to classify and route requests automatically.
- Customer support ticket updates to keep SLAs on track.
Many organizations pair BPA orchestration with RPA bots to address both cross-functional flow and task-level work. For example, a dealership group created a BPA workflow for service orders and used RPA to populate legacy CRM fields — cutting manual entry and improving turnaround, a pattern similar to industry case studies such as the Greenway Auto Group concept referenced in recent reports.
That case shows how combining BPA and RPA delivers quick operational relief plus longer-term process modernization. The next section offers a practical framework to choose the right strategy and explains how Smart Technologies of Florida supports that journey.
How to Choose the Right Automation Strategy for Your Business Needs?
Choosing between RPA and BPA starts with assessing process complexity, integration options, transaction volume, compliance needs, and budget. A practical selection framework begins with discovery and process mining to quantify inefficiencies, then groups processes into quick-win RPA candidates, medium-term BPA redesigns, and hybrid cases that need both. Strong governance, monitoring, and a phased roadmap help ensure automation delivers measurable ROI while avoiding brittle solutions that increase maintenance overhead. This approach balances short-term wins with long-term scalability.
Research into BPA platform evaluation reinforces the need for a structured decision process.
Decision framework for evaluating Business Process Automation (BPA) platforms
This study presents a decision framework to evaluate BPA platforms and help organizations choose tools that match their needs. It combines the Fuzzy Delphi Method (FDM) to refine selection criteria and the Fuzzy Analytic Hierarchy Process (Fuzzy AHP) to prioritize them. Experts from multiple industries validated the approach. Top-ranked criteria include security and compliance, followed by scalability, reliability, and usability. The research also highlights interoperability, cost-effectiveness, and vendor support. The framework is both a methodology for scoring platforms and a practical guide teams can apply directly when selecting BPA solutions.
DEVELOPMENT OF A GENERALIZED DECISION FRAMEWORK FOR THE EVALUATION OF BUSINESS PROCESS AUTOMATION PLATFORMS, I Mahakalanda, 2025
What Factors Should You Consider When Selecting Between RPA and BPA?
Key factors are process standardization, existing integration capabilities (APIs vs. legacy UIs), transaction volume, compliance needs, and in-house maintenance capacity. Well-standardized, high-volume processes with low variability are prime RPA candidates; cross-department workflows with regulatory checks typically require BPA. Consider expected ROI timelines and whether you want fast tactical wins or strategic transformation. Assess risk and governance readiness to avoid “automation debt.”
A structured decision framework mapping scenarios to approaches:
How Does Smart Technologies Support Business Automation with Custom Solutions?
Smart Technologies of Florida provides assessments, custom solution design, and implementations that follow this decision framework. Our Business Process Automation Solutions combine document management, workflow automation, process mining, and enterprise integration so teams can move from discovery to deployment with managed IT, cybersecurity, and office equipment support as needed. We deliver tailored quotes for IT services, cybersecurity, and office equipment, and we prioritize secure, operationally aligned implementations backed by ongoing support.
Beyond automation, Smart Technologies also supplies essential office infrastructure. If you’re upgrading document handling, we offer a range of printers and copiers to keep operations efficient and reliable.
Services and engagement steps we offer:
- Discovery and process mining to prioritize automation targets.
- Custom solution design combining BPA orchestration and RPA where appropriate.
- Managed IT and cybersecurity integration to protect automated workflows.
- Quotes and implementation planning aligned to budget and timelines.
The fragmented nature of BPA knowledge and the need for clear guidance are common challenges organizations face.
Systematic literature review on Business Process Automation frameworks and technologies
This systematic review surveys frameworks, success factors, and technologies in BPA. Analyzing 40 studies from 2019–2024, the authors identified 24 frameworks and 32 key success factors and highlighted the most-used technologies in BPA projects. The review stresses the importance of a strong data culture, executive leadership, change management, targeted technology investment, and a measurable implementation process. Its holistic perspective helps teams plan and execute BPA programs with fewer surprises.
A Systematic Literature Review on Business Process Automation Frameworks and Technologies, C Schieder, 2025
If your team needs an assessment or a tailored quote for an automation roadmap, requesting a consultation from a specialized partner can speed decision-making and reduce risk.
For teams ready to act, Smart Technologies can provide a formal assessment and quote that outlines recommended RPA, BPA, or hybrid approaches, along with managed IT and cybersecurity options to support secure, scalable deployments.
Effective internal and external communication is vital to modern operations. Smart Technologies offers business communication solutions designed to streamline collaboration and connectivity across your organization: learn more.
This guidance prepares teams to pursue prioritized automation projects with a partner that handles both technical integration and the supporting IT and security requirements described above.
When you’re ready to evaluate automation options and request a project quote or assessment, Smart Technologies of Florida positions itself as a transformation partner — helping identify automation targets, design BPA and RPA solutions, and provide managed cybersecurity, IT services, and office equipment support. Our approach emphasizes tailored solutions, comprehensive services, and responsive support to move organizations from pilots to production with measurable outcomes and secure operations. For a formal quote or consultation to begin an automation assessment, engage a qualified provider to turn the decision framework above into an actionable plan.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key considerations when implementing RPA in an organization?
When implementing RPA, evaluate process suitability, governance, and change management. Good RPA candidates are repetitive, rule-based, and stable. Governance is necessary to manage bot lifecycles, monitor performance, and maintain compliance. Change management helps address employee concerns and ensures smooth adoption. Also verify your IT infrastructure can support RPA and provide training so staff can work effectively alongside bots.
How can businesses measure the success of their automation initiatives?
Measure automation success with KPIs like cycle time reduction, error rate, and cost savings, comparing before and after implementation. Track user satisfaction and compliance improvements as well. Regular reviews using these metrics let teams refine automations and ensure projects continue to align with business objectives.
What role does governance play in the success of BPA and RPA?
Governance is critical for both BPA and RPA. It sets accountability, defines compliance guardrails, and enables performance monitoring. Good governance helps ensure processes are well-defined, risks are controlled, and automation supports organizational goals. It also improves stakeholder communication and resource allocation, making it easier to scale automation responsibly.
Can RPA and BPA be integrated, and what are the benefits?
Yes. Integrating RPA and BPA lets RPA handle specific tasks inside the broader workflows orchestrated by BPA. Benefits include better process visibility, fewer manual handoffs, and faster realization of outcomes. Combining both approaches delivers immediate productivity gains while building resilient, scalable processes over time.
What are some common challenges organizations face when adopting automation?
Common challenges include resistance to change, unclear strategy, and integration hurdles. People may worry about job impact or struggle to learn new tools. Without a clear roadmap, automation efforts can be fragmented. Legacy systems can also complicate integration. To succeed, prioritize change management, define clear goals, and ensure strong IT support throughout the project.
How do industry-specific needs influence the choice between RPA and BPA?
Industry needs strongly shape the choice. Highly regulated sectors like healthcare and finance often benefit more from BPA’s process-level controls and governance. Industries with many repetitive, high-volume tasks — such as manufacturing — can get fast wins from RPA. Understanding each industry’s operational realities and regulatory landscape helps teams pick the most effective automation strategy.












